❑An Overview of Earned and Deferred Revenue Tracking
•Earned and Deferred Revenue calculations are a somewhat complex accounting concept (one of many that are designed to ensure full employment for accountants and tax attorneys) but can be summarized as follows:
✓Within the context of the accounting procedures that most of us are familiar, every (Sales) Invoice that is issued would normally be considered "earned" when it is created.
▪As an example: when your Company bills some person or business for something they've purchased, they have already received those parts, services, or repairs from your Company (e.g., the completion of a Work Order, an installation of a new System, etc.).
✓However, when billing for Recurring Revenue (e.g., Monitoring Services for the next Quarter, the upcoming year's Service Contract, next month's Lease Payment), those Sales Invoices are almost never fully "earned" when they are "billed" to the Subscriber.
▪This is because those Invoices for Recurring Services (e.g., Monitoring Fees, Service Contracts, Opening & Closing Reports) are almost always printed and mailed a month (or a least a week or so) in advance of when the Period of Service - for which they are being billed - actually begins.
▪So technically, if the Receipts for those Recurring Revenue Invoices - are posted before the entire period of service (for which they were Invoiced) has ended - which is almost always the case:
oThe Recurring Services that were paid with those Receipts have not yet been provided (or were only been partially provided).
oTherefore, from an accounting standpoint, the Income (i.e., Revenue) which your Company received for those Recurring Services (or at least a portion of that income), could - and probably should - be considered unearned when you received it.
oUnearned Revenue is considered a Company Liability because your Company has received the money, may even have spent the money, but your Company still "owes" that Subscriber some (or all) of those services.
oObviously, once your Company has fully provided those Recurring Services, all of the Recurring Revenues associated those Receipts will have been fully earned (i.e., the previously Unearned service Liability has now been fully provided).
•In summary, Revenue that is Invoiced is not fully Earned until the service - for which the Subscriber was billed - has been fully provided.
✓Therefore, the Company's "books" should reflect in some manner, that the Revenues Received for those Services are Deferred (not recognized as Earnings, and instead are acknowledged as a Liability for services owed but not yet provided), until all of the Invoiced Services for which your Company billed, have actually been provided.
❑Automating the calculation of Earned and Deferred Revenue while using the Fully Automated Recurring Billing feature and/or the manually selected Auto Billing process
1.Fully Automated Recurring Billing feature completely automates the creation of your Company's Recurring Revenue Invoices.
❖This Fully Automated Recurring Billing process makes the Invoicing of your Company's Recurring Revenue a truly "set it and forget it" process.
2.The manually selected Auto Billing process allows you to select which and when selected Billing Cycles will be automatically Invoiced.
3.Billing Cycles - The Billing Cycle Form is used to define when and how your Company's Recurring Revenues are to be Invoiced.
a.Sale Day - The Sale Day field on the Billing Cycle Form is used to construct the Sale Date on the Invoice when billing the Recurring Revenue for each Billing Cycle:
i.Use the Drop-Down Selection List to Choose the Day on which the Bill (Invoice for these Services) will actually be Dated (and created).
ii.The system will not allow a Sale Day Number greater than 28 to be used (because an Recurring Revenue related Invoice with a Sale Day Number greater that 28 would not be generated in February - even if it should have been)
iii.However, it does offer a Last Day of Month option in that Drop-Down Selection List.
b.Period Covered Day - The Period Covered Day field on the Billing Cycle Form is used to identify when the Period of Service actually will begin for this Billing Cycle.
c.Bill In Advance - The Bill In Advance Day field on the Billing Cycle Form is used to identify which (if any) Billing Cycles should be billed a Month in Advance.
•These "Sale Day, "Period Covered Day" and "Bill In Advance" fields in the Billing Cycle Form are used to determine when the First month of a Recurring Revenue Invoice is to be Earned or Deferred.
✓These are the two situations your Company should consider before filling in the "Sale Day, "Period Covered Day" and "Bill In Advance" fields
1.Your Company will be implementing the Fully Automated Recurring Billing feature which allows your Company to specify on what Day (the Sale Day) throughout the month a Subscriber's Recurring Revenue entries (each of which is assigned to a specific Billing Cycle) will be automatically Invoiced.
a.The Sale Day entry in the Billing Cycle Form is used to construct the Sale Date of each Invoice.
b.The Period Covered Day entry in the Billing Cycle Form represents the Day of the Month when the Recurring Service(s) being Invoiced will start being provided.
i.This Period Covered Day may be the same as, or different than, the Sale Day:
ii.The Period Covered description on the Invoice will show a starting day that matches the Period Covered Day (not the Sale Day) and will determine when and how the Earned Revenue is posted
iii.When the Period Covered Day is "1", the First month of service will be fully Earned (fulfilled) within that Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will be posted as Earned on the last day of the first month.
iv.When the Period Covered Day is greater than "1", the First month of service cannot be fully Earned (fulfilled) until the following Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be Earned until the last day of the next month.
c.However, when the Bill In Advance field in the Billing Cycle Form is Checked, the Period Covered Day's starting day is reset to the Month following the Invoice's Sale Date
i.When Bill In Advance is in effect and the Period Covered Day is "1", the First month of service will be fully Earned (fulfilled) in the next Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be posted as Earned until the last day of the next month.
ii.When Bill In Advance is in effect and the Period Covered Day is greater than "1", the First month of service cannot be fully Earned (fulfilled) until the Month following the next Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be posted as Earned until last day of the month after the next month
2.Your Company will not be implementing the Fully Automated Recurring Billing feature, but instead will use the manually selected Auto Billing process in which a specific set of Subscribers who have Recurring Revenue entries assigned to a specific Billing Cycle will be Invoiced for those Recurring Revenues.
a.In this case, using the manually selected Auto Billing process: YOU choose when to create the Invoices for a specifically selected Billing Cycle and YOU manually enter the Sale Date on the Auto Billing Form at the time that process is run.
i.That Sale Date becomes the Sale Date entered on each Invoice.
b.The Period Covered Day entry in the Billing Cycle Form represents the Day of the Month when the Recurring Service(s) being Invoiced will start being provided.
i.The Period Covered description on the Invoice will show a starting day that matches the Period Covered Day (not the Sale Date) and will determine when and how the Earned Revenue is posted
ii.This Period Covered Day may be the same as, or different than the Sale Date:
iii.When the Period Covered Day is "1", the First month of service will be fully Earned (fulfilled) within the Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will be posted as Earned on last day of the first month.
iv.When the Period Covered Day is greater than "1", the First month of service cannot be fully Earned (fulfilled) until the following Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be posted as Earned until the last day of the next month.
c.However, when the Bill In Advance field in the Billing Cycle Form is Checked, the Period Covered Day's starting day is reset to the following Month.
i.When Bill In Advance is in effect and the Period Covered Day is "1", the First month of service will be fully Earned (fulfilled) in the next Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be posted as Earned until the last day of the next month.
ii.When Bill In Advance is in effect and the Period Covered Day is greater than "1", the First month of service cannot be fully Earned (fulfilled) until the Month following the next Month, therefore the first month's Revenue will not be posted as Earned until the Month after the next Month.
3.Your Company may use a combination of both the Fully Automated Recurring Billing and the manually selected Auto Billing processes, if your Company's business model requires it.
A.For General Ledger System Users - When Earned and Deferred Revenues are being tracked, the Sale Day and Period Covered Day (as described above) in combination with the Bill In Advance setting of the Billing Cycle are used to determine when the Recurring Revenue is to be Earned.
1.This Earned (or Deferred) Revenue is calculated automatically when using either the Fully Automated Recurring Billing feature and/or the manually selected Auto Billing process, and will be posted appropriately (following the situations discussed above) by using the Post Earned Revenue procedure.
2.Earned Revenue should be posted to the General Ledger System - using the Post Earned Revenue process - on or after the Last Day of the selected Month being posted.
B.For General Ledger System Users - When Earned and Deferred Revenues are being tracked:
1.The Gross Amount (including Sales Tax, if charged) of each Recurring Revenue Sale is Debited (added) to the Accounts Receivable Asset Account (a Mandatory Account).
2.The Net Amount (not including any Sales Tax) is Credited (added) to the associated Deferred Revenue Liability Account
3.If Sales Tax was charged, the Amount of that sales tax is Credited (added) to the appropriate Sales Tax Payable Liability Account (i.e., Local Tax, National Tax, or both, as needed).
4.Then, once each month, the Post Earned Revenue dialog is used to calculate the Earned Recurring Revenue for a selected Accounting Period. during which:
a.The Deferred Revenue Liability Account is Debited (reduced) by the Value of the Recurring Revenue that was Earned during the Accounting Period
b.The Sales Account assigned to the Recurring Revenue Item is Credited (increased) by the Value of the Recurring Revenue that was Earned during the Accounting Period
c.The Current Earnings Equity Account (a Mandatory Account) is Credited (increased) by the Value of the Recurring Revenue that was Earned during the Accounting Period
d.The Earnings Posting Expense Account (a Mandatory Account) is Debited (increased) by the Value of the Recurring Revenue that was Earned during the Accounting Period
C.For General Ledger System Users - When Earned and Deferred Revenues are not being tracked:
1.The Net Amount (not including any Sales Tax) is Credited (added) to the associated Sales Account (assigned to that Recurring Revenue Item).
2.The Gross Amount (including Sales Tax, if charged) of each Recurring Revenue Sale is Debited (added) to the Accounts Receivable Asset Account (a Mandatory Account).
3.If Sales Tax was charged, the Amount of that sales tax is Credited (added) to the appropriate Sales Tax Payable Liability Account (i.e., Local Tax, National Tax, or both, as needed).
4.The Net Amount (not including any Sales Tax) is Credited (added) to the Current Earnings Equity Account (a Mandatory Account).
5.The Net Amount (not including any Sales Tax) is Debited (added) to the Earnings Posting Account (a Mandatory Account).
✓Please read the Understanding Earned and Deferred Revenue chapter in the General Ledger section of these Help Files.
❑This Deferred Revenue Setup menu option only appears when the DeferRecurringRevenue option is set to False ("F") in Company Settings dialog which is accessible from the Company tab of the User Options Form.
•The Deferred Revenue Setup procedure is used to properly initialize the Deferred & Earned Recurring Revenue feature within the MKMS Accounts Receivable module and - if the General Ledger module is Registered - in the General Ledger System.
➢Note: Before running the Deferred Revenue Setup Wizard, go into Company Settings and set the Bill in Advance option ("BillInAdvance") to False ("F").
Thereafter, you will use the Billing Cycles Form to individually set each Billing Cycle entry to Bill In Advance, or not to Bill In Advance, as needed, based on your Company's business model.
•Once this Deferred Revenue Setup procedure is executed properly, the option no longer appears in this menu.
a.The DeferRecurringRevenue option is automatically set to True ("T") in the Company Settings dialog.
b.Earned and Deferred Revenues are tracked for each Recurring Revenue Detail Line Item on those type of Invoices created within the Accounts Receivable module
c.These Financial Transactions will also be recorded in the General Ledger System using the Post Earned Revenue dialog which will be used to periodically calculate, distribute, and post Earned Revenues to the appropriate General Ledger Accounts, the Transaction File, and the Account Register.
d.The Deferred Revenue report lists those Deferred Revenues that will automatically be calculated and posted as part of the Recurring Revenue Billing procedure.
e.The Earned Revenue by Month report tells your Company how much of that previously Deferred Revenue has subsequently been Earned in a User specified Month (or Year).
•For General Ledger System Users - If there are any records currently in the Suspended Invoicing Section of any Recurring Revenue items, during this Deferred Revenue Set Up process, those records will be managed as a standard Sale (they will be assigned to the General Ledger Account associated with its Sale-Purchase Item ) - not as a deferred Recurring Revenue item.
✓Why?
1)The system does not know exactly when the Suspended Invoice item will be added to a future Invoice;
2)Suspended Invoice items are ignored on the Earned and/or Deferred Recurring Revenue related reports;
3)They are also ignored during the "Post Earned Revenues" process for reason # 1).
▪Therefore it does the safe thing by assuming these Suspended Invoice items are immediately Earned.
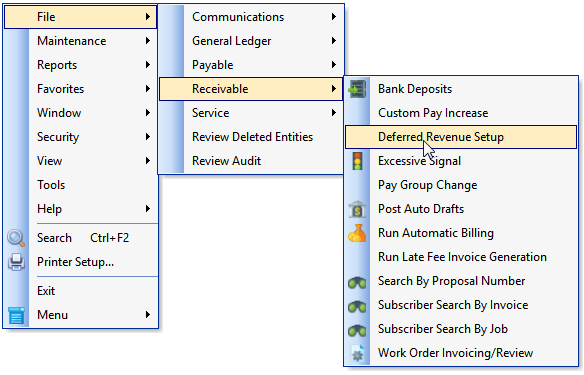
•To open the Deferred Revenue Setup Form:
a)From the Backstage Menu System Select File and Choose Receivable and Select the Deferred Revenue Setup option, or
b)From the Quick Access Menu, Select File and Choose Receivable and Select the Deferred Revenue Setup option
•The Deferred Revenue Setup Wizard will ensure that all of the components that are necessary to Calculate Deferred Revenue are properly set.

Deferred Revenue Setup - Start up Screen
✓Click the Next button to proceed.
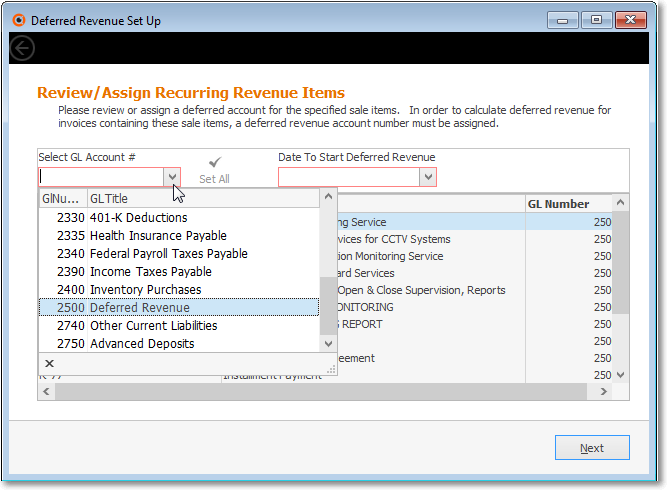
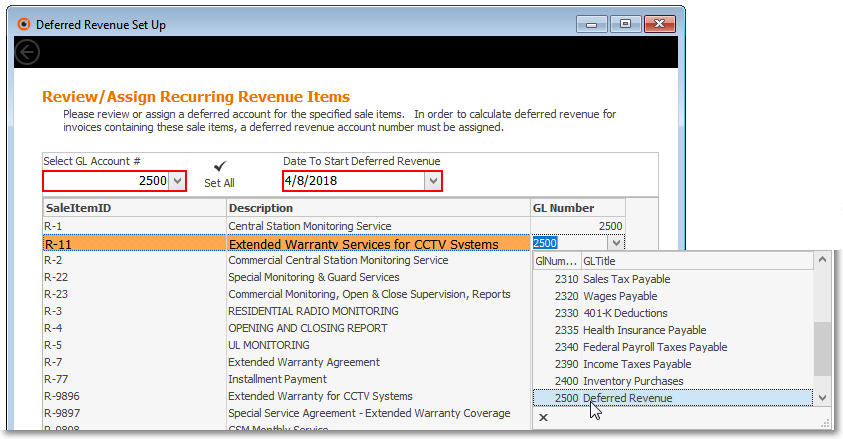
•Review/Assign Recurring Revenue Items dialog - All Recurring Revenue Sale-Purchase Items are listed, along with the Deferred Revenue Liability General Ledger Account Number that was (if it was) assigned to each.
✓Select GL Account # - Using the Drop-Down Selection List provided, Choose the Deferred Revenue Liability created for that purpose in the General Ledger Accounts Form.
Deferred Revenue Setup - Review/Assign Recurring Revenue Items Screen - Select GL Account # field
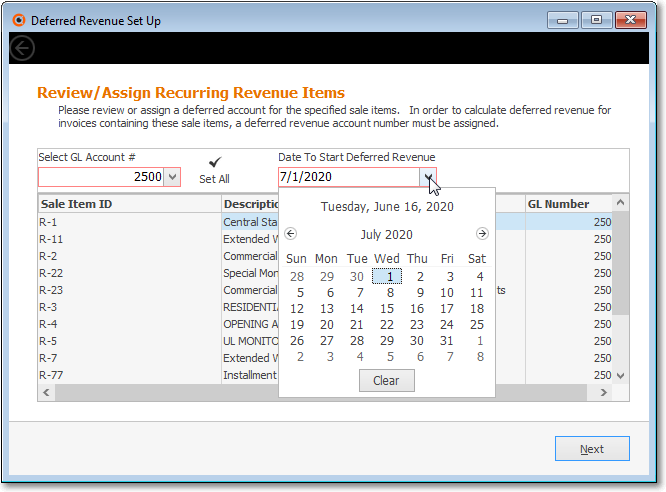
✓Date To Start Deferred Revenue - Use the Drop-Down Calendar/Date Entry field provided to Choose the desired Date when you want to start tracking your Company's Deferred Revenue
Deferred Revenue Setup - Review/Assign Recurring Revenue Items Screen - Date To Start Deferred Revenue field
•Recurring Revenue Items List: As illustrated above, all of the existing Recurring Revenue Sale-Purchase Items are included in the list.
✓Sale Item ID - This column lists each Recurring Revenue Sale-Purchase Item
✓Description - This column lists the associated Description of each Recurring Revenue Sale-Purchase Item
✓GL Number - This column displays the current Deferred Revenue Liability General Ledger Account Number assigned to each Recurring Revenue Sale Item
•(Re-)Setting the appropriate Deferred Revenue Liability General Ledger Account Number
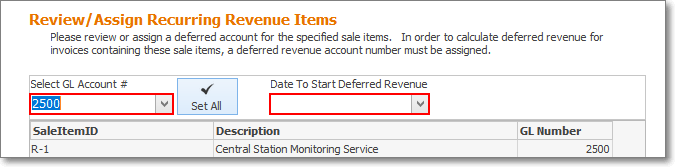
✓Set All - Click this option to assign the selected Deferred Revenue Liability General Ledger Account Number to all Recurring Revenue Sale-Purchase Items
✓Optionally, as shown below, a GL Number may be assigned or modified for any listed GL Number - one at a time.
✓Click the Next button to continue.
•Reviewing the Account Balances that will be affected by the changes made in the Review/Assign Recurring Revenue Items dialog:
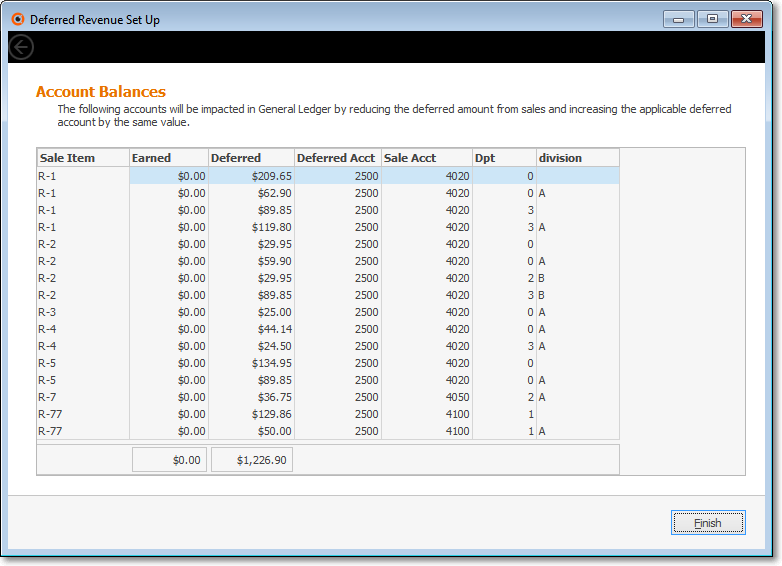
✓If any Account Balances will be affected by the addition of and/or changes to the Deferred Revenue Liability General Ledger Account Number, those will be listed in the Form illustrated above.
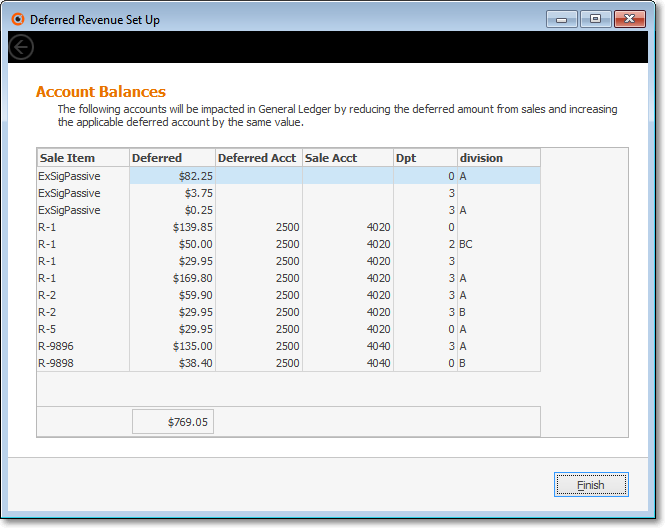
•Click the Finish button when done.
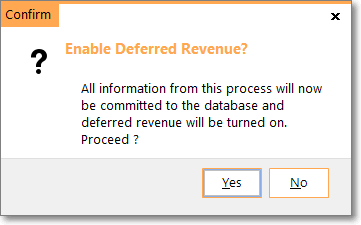
Confirm - Enable Deferred Revenue?
✓Click the Yes button to Confirm that this is required.
![]()
Complete! Deferred Revenue tracking is now active.
▪Click the OK button to acknowledge the successful completion of the Deferred Revenue Setup procedure
▪As indicated, the User must Logout and then Log In again to fully activate the Deferred Revenue process.
✓The Defer Recurring Revenue ("DeferRecurringRevenue") option in Company Settings will be set to True ("T").
•The Earned and Deferred Revenue Calculations will now be managed by MKMS (see the "Automating the calculation of Earned and Deferred Revenue" discussion above).